Components of a Calibration Certificate
Measurement Uncertainty Example
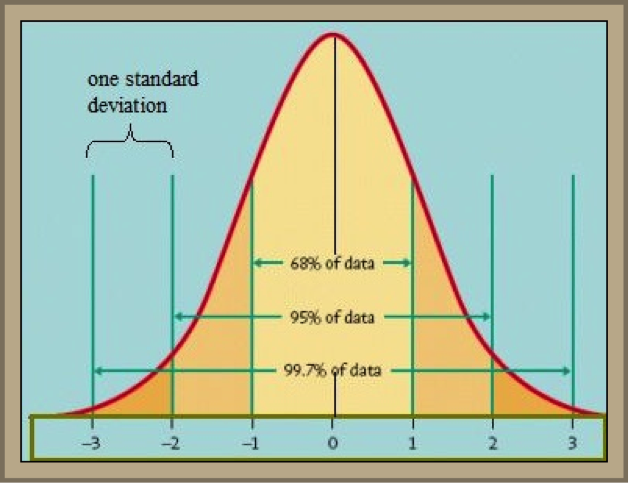
As an example, let us take some values from our example certificate for a temperature probe. When a standard temperature gage reads 100.00 C, the probe indicated a value of 100.0 C. This looks as if the probe has no error, however the uncertainty of measurements is given as ± 0.5 C, and the confidence level is given as 95%.
The English translation of these figures would read as follows: When I apply exactly 100 C on my probe, it will read somewhere between 99.5 C and 100.5 C, 95% of the time.
Only 95% of the time? What about the other 5%, you ask. Well, if the calibration laboratory has done its calculations correctly then statistically one measurement in every 20 may fall outside of the ±0.5 C. This is why it is important to take multiple measurements if you want accurate results.
Reference should be made to such literature for further information about the calculations of uncertainties of measurement.
